Diferencia entre revisiones de «Usuario:Wendy»
Sin resumen de edición |
Sin resumen de edición |
||
| (No se muestran 8 ediciones intermedias del mismo usuario) | |||
| Línea 8: | Línea 8: | ||
--[[Usuario:Wendy|Wendy]] 01:53 22 sep 2009 (UTC) | --[[Usuario:Wendy|Wendy]] 01:53 22 sep 2009 (UTC) | ||
[[Demostración]] | |||
---- | |||
== EJERCICIOS == | |||
'''1.- Hallar Z tales que:''' | |||
A) <math>\displaystyle {e^{z}=-2}</math> | |||
SOLUCION | |||
Escribimos <math>\displaystyle {e^{z}}</math> como <math>\displaystyle {e^{x}}{e^{iy}}</math> | |||
<math>\displaystyle {e^{x}}{e^{iy}=\rho{e^{i\phi}}}</math> | |||
<math>\displaystyle {\rho=e^{x}=|e^{z}|=2}</math>, por lo que <math>\displaystyle {x=\ln2}</math> | |||
Ahora para <math>\displaystyle{y}</math> | |||
<math>\displaystyle {e^{iy}=e^{i\phi}=-1}</math>; para que esto se cumpla <math>\displaystyle {\phi=\pi+2n\pi}</math> | |||
Finalmente | |||
<center><math>\displaystyle {z=\ln2+{{(2n+1)}\pi}i}</math></center> | |||
B) <math>\displaystyle {e^{2z-1}=1}</math> | |||
SOLUCION | |||
Escribimos | |||
<math>\displaystyle {e^{2x+2iy-1}=1}</math> | |||
<math>\displaystyle {e^{2x-1}}{e^{2iy}=\rho{e^{i\phi}}}</math> | |||
donde <math>\displaystyle {\rho=1}</math> | |||
y para que esto se cumpla <math>\displaystyle {e^{2x-1}=1}</math> | |||
entonces <math>\displaystyle {2x-1=0}</math>; por lo tanto <math>\displaystyle {x=\frac{1}{2}}</math> | |||
Ahora para <math>\displaystyle{y}</math> | |||
<math>\displaystyle {e^{2iy}=e^{i\phi}=1}</math>; esto es <math>\displaystyle {2y=0+(2n\pi)}</math> | |||
Finalmente | |||
<center><math>\displaystyle {z=\frac{1}{2}+{n\pi}i}</math></center> | |||
'''2.-Evaluar la siguiente integral <math>\int_{\,0}^{\,\frac{\pi}{6} }\,{{e}^{2i\,t}}\,dt</math>''' | |||
SOLUCION | |||
Denotemos la integral anterior con <math>\displaystyle {Int}</math>; entonces | |||
<math>Int=\frac{{e}^{2i\,t}}{2i}\biggr|_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{6}}</math> | |||
<math>Int=\displaystyle {\frac{e^{2i\frac{\pi}{6}}}{2i}-\frac{1}{2i}}</math> | |||
<math>Int=\displaystyle{\frac{1}{2i}}[{{\cos(\frac{\pi}{3})+{i}\sin(\frac{\pi}{3})-1}]}</math> | |||
<center><math>Int=\displaystyle{\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}+\frac{i}{4}}</math></center> | |||
'''3.-Muestre que <math>\int_{\,0}^{\,2\pi }\,{{e}^{im\,\theta}}\,{{e}^{-in\,\theta}}\,d\theta</math> es 0 si m=n y vale <math>\displaystyle{2\pi}</math> si m es diferente de n''' | |||
SOLUCION | |||
<math>\int_{\,0}^{\,2\pi }\,{{e}^{im\,\theta}}\,{{e}^{-in\,\theta}}\,d\theta=\int_{\,0}^{\,2\pi }\,{{e}^{i(m-n)\,\theta}}\,d\theta</math> | |||
Denotemos el resultado anterior como <math>\displaystyle {Int}</math>; entonces | |||
<math>Int=\frac{{e}^{i(m-n)\,\theta}}{i(m-n)}\biggr|_{0}^{2\pi}</math> | |||
<math>Int=\displaystyle{\frac{1}{i(m-n)}-\frac{1}{i(m-n)}}</math> | |||
<math>Int=\displaystyle{0}</math> | |||
pero cuando m=n | |||
<center><math>Int=\int_{\,0}^{\,2\pi }\,d\theta=2\pi</math></center> | |||
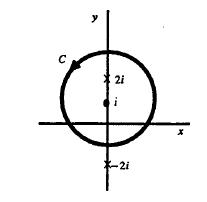
'''4.-Encuentre el valor de la integral <math>\displaystyle{g(z)=\frac{1}{(z^{2}+4)^2}}</math> de alrededor del círculo <math>\displaystyle{|z-i|=2}</math>''' | |||
[[Archivo:curva.jpg]] | |||
SOLUCION | |||
Podemos escribir la integral de <math>\displaystyle{g(z)}</math> como: | |||
<math>Int=\displaystyle{\int_{\,C}\,\frac{\frac{1}{(z+2i)^2}}{(z-2i)^2}dz}</math> | |||
si <math>{\displaystyle f^{k}\left(z\right)={\displaystyle \dfrac{k!}{2\Pi i}\int_{\gamma}\dfrac{f\left(w\right)}{\left(w-z\right)^{k+1}}}dw}</math> | |||
con <math>\displaystyle k=1</math> | |||
entonces | |||
<math>Int=\displaystyle{\frac{2i\pi}{1!}\frac{d}{dz}\frac{1}{(z+2i)^2}\biggr|_{z=2i}}</math> | |||
<math>Int=\displaystyle{2i\pi\frac{-2}{(z+2i)^3}\biggr|_{z=2i}}</math> | |||
<math>Int=\displaystyle{\frac{-4i\pi}{(4i)^3}}</math> | |||
<math>Int=\displaystyle{\frac{\pi}{16}}</math> | |||
Revisión actual - 03:11 9 dic 2010
WENDY CAROLINA GONZALEZ OLIVARES
VARIABLE COMPLEJA
E-MAIL: shelylgk@hotmail.com
--Wendy 01:53 22 sep 2009 (UTC) Demostración
EJERCICIOS
1.- Hallar Z tales que:
A)
SOLUCION
Escribimos como
, por lo que
Ahora para
; para que esto se cumpla
Finalmente
B)
SOLUCION
Escribimos
donde
y para que esto se cumpla
entonces ; por lo tanto
Ahora para
; esto es
Finalmente
2.-Evaluar la siguiente integral
SOLUCION
Denotemos la integral anterior con ; entonces
3.-Muestre que es 0 si m=n y vale si m es diferente de n
SOLUCION
Denotemos el resultado anterior como ; entonces
pero cuando m=n
4.-Encuentre el valor de la integral de alrededor del círculo
SOLUCION
Podemos escribir la integral de como:
si
con
entonces
























![Int=\displaystyle{\frac{1}{2i}}[{{\cos(\frac{\pi}{3})+{i}\sin(\frac{\pi}{3})-1}]}](https://en.wikipedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0b6cff824da6ea9dd81ce404552c251b6531614a)